Have you ever wondered how entering the world’s second-largest economy could transform your business? China, with its 1.4 billion people and rapid economic growth, offers huge opportunities for exporters.
Exporting to China can boost your profits and diversify your revenue. The growing middle class and the Belt and Road Initiative drive demand for high-quality imports, making China an attractive market.
This guide provides a roadmap for exporting to China, offering practical tips and insights to help you navigate trade regulations, find the right partners, and succeed in this dynamic market. Let’s empower your business in China.
I. Understanding the Chinese Market
Overview of China’s Economic Landscape

China’s economy is booming, with a GDP growth rate that has averaged around 6% annually over the past decade. In 2021, China’s GDP was approximately $17.7 trillion, solidifying its position as the world’s second-largest economy. Major urban centers like Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen are hubs of economic activity, driving innovation and consumption. These cities contribute significantly to the country’s GDP, with Shanghai alone accounting for over 3.6%. The government’s focus on modernization and infrastructure development, including projects like the Belt and Road Initiative, continues to fuel economic expansion, making China a prime destination for exporters.
Key Industries and Consumer Trends
Several key industries are thriving in China, including technology, manufacturing, and consumer goods. The tech sector has seen explosive growth, with companies like Alibaba and Tencent leading the way. In 2021, China’s tech industry was valued at over $2.1 trillion. Consumers in China are increasingly tech-savvy and brand-conscious, seeking high-quality, innovative products. The rise of e-commerce platforms like JD.com and Tmall has revolutionized the retail landscape, making it easier for foreign brands to reach Chinese consumers. These platforms saw a combined sales volume of over $1 trillion in 2020. Additionally, there’s a growing demand for health and wellness products, driven by an aging population and a greater focus on healthy lifestyles. The health and wellness market in China is projected to reach $70 billion by 2025.
Identifying Export Opportunities in China
To succeed in the Chinese market, it’s crucial to identify export opportunities that align with local demand. Products that cater to the tastes and preferences of Chinese consumers are more likely to succeed. For instance, there is a strong market for luxury goods, organic foods, and sustainable products. The luxury goods market in China was valued at $54 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow annually by 5.4%. Understanding regional differences is also key; while coastal cities may favor premium products, inland regions may have different preferences. By conducting thorough market research and leveraging local insights, exporters can uncover lucrative opportunities and tailor their strategies to meet the specific needs of the Chinese market. Utilizing resources like the China-Britain Business Council or the American Chamber of Commerce in China can provide valuable market data and networking opportunities.
II. Market Entry Strategies
Assessing Market Potential and Competition
Before entering the Chinese market, it’s essential to assess market potential and analyze the competition. Start by researching market size, growth trends, and consumer behavior. According to the World Bank, China’s GDP grew by 8.1% in 2021, indicating significant market potential. Tools like market reports and industry analysis can provide valuable insights. Look at competitors to understand their strategies and identify gaps you can fill. For example, if local brands dominate the market, find a unique selling proposition that sets your product apart. In 2020, foreign brands accounted for only 20% of the Chinese retail market, highlighting opportunities for differentiation. Understanding your competition helps you position your product more effectively and capture market share.
Developing an Export Strategy
A well-crafted export strategy is crucial for success in China. Begin by defining your target audience and setting clear objectives. Outline your marketing, sales, and distribution plans. Consider factors like pricing, product adaptation, and regulatory compliance. It’s important to localize your marketing efforts to resonate with Chinese consumers. For example, using popular social media platforms like WeChat (with over 1.2 billion users) and Weibo can enhance your brand visibility. Additionally, leverage data to make informed decisions and adjust your strategy as needed. A flexible and responsive approach will help you navigate the complexities of the Chinese market. According to a McKinsey report, localized marketing can increase brand engagement by up to 30%.
Finding Distributors and Partners in China
Identifying reliable distributors and partners is vital for market entry. Conduct thorough due diligence to ensure potential partners have a good reputation and the necessary infrastructure to support your product. Networking events, trade shows, and industry associations are excellent resources for finding reputable distributors. Platforms like Alibaba and Global Sources can also connect you with potential partners. Building strong relationships with your distributors is key; regular communication and clear agreements can help prevent misunderstandings and ensure smooth operations. In 2021, over 70% of foreign businesses in China reported that having a local partner significantly eased market entry and operations.
Tips for Successful Market Entry
To ensure a successful market entry, focus on understanding and adapting to local preferences. Here are some key tips:
- Cultural Sensitivity: Respect and understand Chinese culture. This includes adapting your product and marketing to meet local tastes.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stay updated on Chinese regulations and ensure your products meet all requirements to avoid legal issues.
- Local Partnerships: Leverage local expertise by partnering with Chinese companies who understand the market dynamics.
- Customer Engagement: Engage with consumers through local social media and e-commerce platforms to build brand loyalty.
- Continuous Learning: Keep learning and adapting based on market feedback and changes.
By following these strategies, you can enhance your chances of successfully entering the Chinese market and achieving sustainable growth.
III. China Trade Policies and Compliance
Overview of China’s Trade Policies

China’s trade policies are designed to promote economic growth and protect domestic industries. The government has implemented measures such as free trade zones and export incentives. For example, China’s 21 Free Trade Zones (FTZs), including the Shanghai FTZ, offer reduced tariffs and simplified customs procedures to encourage international trade. According to the Ministry of Commerce, these FTZs accounted for over 12% of China’s total foreign trade in 2021. Understanding the basics of China’s trade policies is essential for businesses to navigate the market effectively and ensure compliance with local regulations.
Understanding Trade Barriers and Tariffs
Trade barriers and tariffs can significantly impact your ability to export to China. These barriers include import duties, quotas, and licensing requirements. For instance, China imposes tariffs on certain goods, such as a 25% tariff on automobiles, to protect local industries and manage the balance of trade. The World Trade Organization (WTO) reports that China’s average tariff rate was 9.8% in 2021. Identifying these barriers early is crucial. Tools like the WTO database and Chinese government resources provide valuable information on current tariffs and trade barriers. By understanding these obstacles, you can develop strategies to mitigate their impact and optimize your export processes.
Navigating Chinese Export Laws and Regulations
Navigating Chinese export laws and regulations is essential for successful market entry. China has stringent regulations governing the import and export of goods, including quality standards, certification requirements, and customs procedures. For example, electronics and pharmaceuticals must comply with specific Chinese standards and obtain necessary certifications, such as the China Compulsory Certification (CCC). In 2021, non-compliance with CCC standards led to the detention of over 20,000 products at Chinese customs. Working with local experts and utilizing resources like the CCC can help ensure your products meet all legal requirements. Staying compliant with these regulations facilitates smoother transactions and builds trust with Chinese partners and customers.
IV. Chinese Customs Regulations
Essential Customs Procedures and Documentation
 Navigating Chinese customs requires a thorough understanding of customs procedures and documentation. Essential documents include a bill of lading, commercial invoice, packing list, and a certificate of origin for certain products. According to the General Administration of Customs of China (GACC), proper documentation is crucial for smooth customs clearance. Errors can lead to delays and additional costs. In 2020, over 30% of customs clearance delays were due to incorrect documentation. Utilize resources like the China Customs website to stay updated on requirements.
Navigating Chinese customs requires a thorough understanding of customs procedures and documentation. Essential documents include a bill of lading, commercial invoice, packing list, and a certificate of origin for certain products. According to the General Administration of Customs of China (GACC), proper documentation is crucial for smooth customs clearance. Errors can lead to delays and additional costs. In 2020, over 30% of customs clearance delays were due to incorrect documentation. Utilize resources like the China Customs website to stay updated on requirements.
Import Duties and Taxes
China imposes import duties and taxes on various products. These include customs duties, value-added tax (VAT) (typically 13%), and sometimes consumption tax. For example, electronics might have a duty rate of 10%, while textiles might be 15%. Accurate calculation of these costs is crucial for competitive pricing. According to the WTO, China’s average applied tariff rate was 9.8% in 2021. Tools like the China Import Tariff database can help you determine specific rates, ensuring your products are competitively priced and your business remains profitable.
Compliance with Chinese Standards and Certifications
Ensuring your products meet Chinese standards and obtain necessary certifications is critical. The China Compulsory Certification (CCC) is required for products like electronics and toys. In 2021, over 20,000 products were detained at Chinese customs due to non-compliance with CCC standards. Partner with local experts and use services like the China Certification and Inspection Group (CCIC) to streamline this process. Compliance not only facilitates smoother market entry but also builds trust with Chinese consumers and partners, enhancing your brand’s reputation.
V. Export Documentation and Requirements
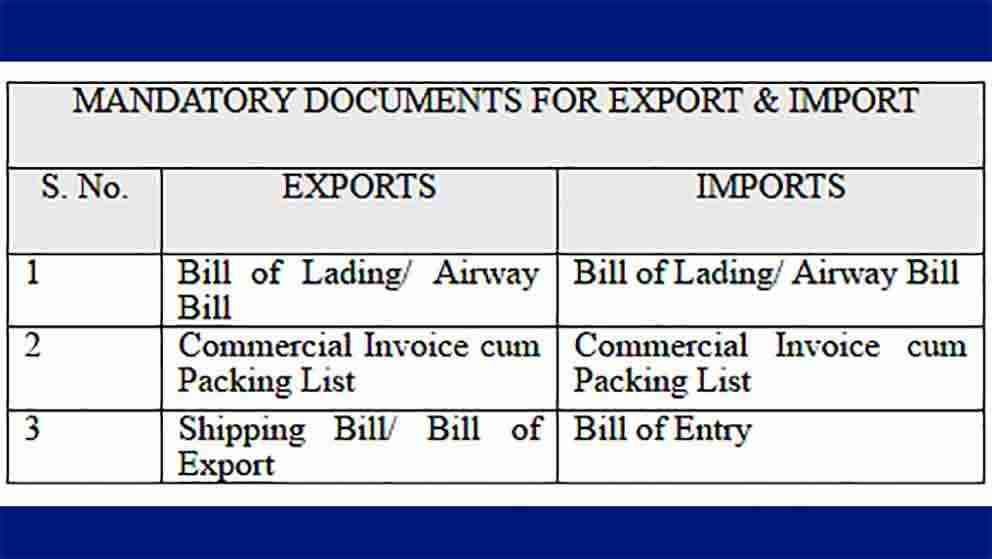
 List of Essential Export Documents
List of Essential Export Documents
When exporting to China, having the right documentation is crucial for smooth customs clearance. Key documents include:
- Commercial Invoice: Details about the goods, their value, and terms of sale. In 2021, inaccurate invoices caused 25% of customs delays.
- Bill of Lading: Proof of shipment and receipt of goods. It’s a critical document for logistics.
- Packing List: Specifies the contents of each package, necessary for customs inspection.
- Certificate of Origin: Verifies the product’s origin, required for tariff calculations.
- Import/Export License: Authorization for the trade of specific goods, especially for regulated items.
- Inspection Certificate: Ensures the goods meet Chinese standards, particularly for food and pharmaceuticals.
- Insurance Certificate: Coverage for the goods during transit, mitigating risk.
Having these documents accurately prepared ensures compliance and helps avoid delays.
Step-by-Step Guide to Preparing Documentation
Preparing export documentation involves several critical steps:
- Gather Information: Collect all necessary details about the goods, including descriptions, quantities, and values. Use standardized formats to avoid errors.
- Create the Commercial Invoice: Ensure it includes all required information, such as buyer and seller details, payment terms, and itemized list of goods. This document must be precise to prevent valuation disputes.
- Prepare the Bill of Lading: Coordinate with your shipping company to generate this document, which confirms shipment and delivery terms.
- Draft the Packing List: Include detailed information about the packaging, including weight and dimensions. This aids customs officials in verifying shipments.
- Obtain Certificates: Apply for the Certificate of Origin and any necessary inspection certificates from relevant authorities, like the China Inspection and Quarantine (CIQ).
- Secure the Import/Export License: Verify whether your product requires a special license and apply if needed. High-value and sensitive goods often require additional permits.
- Arrange Insurance: Obtain an insurance certificate to cover potential risks during transit, ensuring protection against loss or damage.
Following these steps helps ensure your documents are complete and accurate, facilitating a smoother export process.
Tips for Ensuring Smooth Customs Clearance
To achieve smooth customs clearance, follow these tips:
- Double-Check Documentation: Ensure all documents are complete and accurate. Errors can lead to delays and additional costs. In 2020, over 30% of export delays were due to documentation issues.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with the latest Chinese customs regulations and requirements to avoid non-compliance. Regulatory changes are frequent, particularly in the tech and health sectors.
- Use Professional Services: Consider hiring a customs broker to navigate complex regulations and paperwork. Professional services can reduce clearance times by up to 40%.
- Communicate Clearly: Maintain open communication with your Chinese import partners to address any issues promptly. Miscommunication can lead to shipment rejections.
- Prepare for Inspections: Ensure your goods meet all Chinese standards and are ready for potential inspections. Non-compliance can result in fines or shipment returns.
By following these tips, you can minimize delays and ensure a seamless entry of your products into the Chinese market.
VI. Trade Compliance and Legal Considerations
 Understanding China Trade Compliance Requirements
Understanding China Trade Compliance Requirements
Navigating China’s trade compliance requirements is essential for exporters. Compliance involves adhering to import regulations, product standards, and customs procedures. China mandates specific requirements for product labeling, safety certifications, and quality standards. For example, electronics must comply with the China Compulsory Certification (CCC) standards. According to the China General Administration of Customs, failure to meet these standards can result in shipment delays or rejections, impacting your market entry strategy.
Key Legal Considerations for Exporters
Understanding the key legal considerations is crucial when exporting to China. Contracts should be clear and comply with Chinese law. Protecting intellectual property (IP) is vital; registering trademarks and patents in China can prevent IP infringement. According to the World Intellectual Property Organization, China accounted for 46.4% of global patent applications in 2020, highlighting the importance of IP protection. Additionally, be aware of anti-bribery laws and ensure all business practices comply with Chinese regulations. Employing a local legal advisor can provide invaluable insights and help navigate these complexities.
Best Practices for Trade Compliance
Adopting best practices for trade compliance can streamline your export process and mitigate risks. Maintain accurate records of all transactions and compliance documents. Regularly update your knowledge of changing regulations to stay compliant. Engage with local experts who understand the regulatory landscape. Implement a robust compliance program within your organization, including regular training for your team on trade regulations and legal requirements. By following these practices, you can ensure a smoother, more efficient entry into the Chinese market.
VII. Best Practices for Exporting to China
Tips for Successful Exporting to China
To succeed in exporting to China, follow these key tips. First, conduct thorough market research to understand local consumer preferences and cultural nuances. According to McKinsey, 76% of Chinese consumers prefer products tailored to their tastes. Next, establish a strong online presence. With over 1 billion internet users, leveraging platforms like WeChat (used by 78% of Chinese internet users) and Tmall can significantly boost visibility. Finally, build reliable relationships with local partners and distributors, as trust is crucial in Chinese business culture. For example, companies that invest time in relationship-building often see better long-term success.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Exporting to China involves overcoming several common challenges. One major challenge is navigating regulatory compliance. China’s regulations can be complex and frequently changing; staying updated is essential. According to the World Bank, China ranks 31st in ease of doing business due to its regulatory environment. Another challenge is protecting intellectual property (IP). Registering your IP in China can prevent infringement; the World Intellectual Property Organization reported that China accounted for 46.4% of global patent applications in 2020. Understanding and adapting to local competition is also crucial. Differentiating your product through quality, price, or unique features helps in a competitive market. Managing logistics and supply chains efficiently can be difficult due to China’s vast geography; partnering with reliable local logistics providers is recommended.
Case Studies of Successful Exporters
Examining successful exporters can provide valuable insights. For example, Apple Inc. successfully entered the Chinese market by adapting its products and establishing a strong retail presence in major cities. According to Statista, Apple held a 16% market share in China in 2020. Starbucks tailored its menu to include local flavors and conducted extensive market research to understand Chinese consumer behavior, resulting in over 5,000 stores across China as of 2021. Another example is Zara, which achieved success by rapidly adjusting its inventory to match fast-changing fashion trends, demonstrating the importance of localization, market research, and agility.
VIII. Exporting Specific Products to China
Step-by-Step Guide to Exporting Agricultural Products
Exporting agricultural products to China involves several important steps. First, ensure your products meet China’s strict import regulations. The General Administration of Customs China (GACC) requires specific phytosanitary certificates and quarantine inspections. For example, in 2020, China imported $133.1 billion in agricultural products, reflecting the importance of compliance. Second, identify reliable local partners. Working with experienced importers can help navigate regulations and distribution channels. Third, adapt your packaging and labeling to meet Chinese standards. Labels must be in Chinese and include detailed product information. Finally, use local marketing strategies to appeal to Chinese consumers. Highlighting the quality and safety of your agricultural products can significantly enhance their market appeal.
Exporting Consumer Electronics to China
The consumer electronics market in China is vast, but entering it requires careful planning. First, ensure your products comply with the China Compulsory Certification (CCC) standards. Without this certification, electronics cannot be sold in China. In 2020, China imported $634 billion worth of electronic products, underscoring the market potential. Next, partner with local e-commerce platforms like JD.com and Tmall to reach a broad audience. Chinese consumers prefer buying electronics online, making these platforms crucial for market entry. Third, offer after-sales service and support in Chinese. Providing excellent customer service can enhance your brand reputation and loyalty. Lastly, protect your intellectual property by registering patents and trademarks in China to prevent infringement.
Industry-Specific Requirements and Strategies
Each industry has specific requirements and strategies for exporting to China. For instance, the food and beverage industry requires compliance with the Chinese National Standards (GB standards). Products must pass safety tests and be labeled correctly. The cosmetics industry faces stringent regulations, including mandatory animal testing for imported cosmetics, though recent reforms are changing these requirements. For the automotive industry, meeting China’s emissions standards and safety regulations is essential. Adopting localized marketing strategies that resonate with Chinese consumers is critical across all industries. For example, highlighting eco-friendly features can be particularly effective in appealing to environmentally conscious buyers. Understanding these industry-specific nuances can significantly enhance your success in the Chinese market.
IX. Preparing Your Business for Exporting
Assessing Your Business Readiness
Before exporting to China, it’s crucial to assess your business readiness. Start by evaluating your current capacity to handle increased demand. Can your production line scale up if orders surge? A study by the International Trade Centre revealed that 68% of small businesses struggle with scaling up for export markets. Next, consider your export knowledge. Are your team members familiar with international trade regulations and logistics? Finally, assess your financial health. Ensure you have the necessary funds to cover upfront costs, such as production, shipping, and marketing expenses. According to a survey by the Small Business Administration, 58% of small businesses face significant financial barriers when entering new markets.
Building an Export Plan
A well-structured export plan is essential for success in the Chinese market. Begin by defining your target market. Which regions in China are most likely to demand your product? Use data and market research to pinpoint these areas. For instance, coastal cities like Shanghai and Guangzhou are known for higher consumption of imported goods. Next, outline your marketing strategy. How will you position your product? Platforms like WeChat and Weibo are effective for digital marketing in China, with WeChat boasting over 1.2 billion monthly active users. Additionally, establish your logistics and distribution plan. Decide whether you’ll use local distributors or manage logistics independently. Collaborating with logistics companies like SF Express can streamline the distribution process, as they have extensive networks across China.
Financial Considerations and Funding Options
Exporting to China requires careful financial planning. Calculate all potential costs, including production, shipping, tariffs, and marketing expenses. Understanding the payment terms preferred in China, such as letters of credit or open account terms, is crucial. To support your export activities, explore funding options. Government programs, such as the Export-Import Bank of the United States (EXIM), offer loans and insurance to exporters. For example, EXIM provided $8.2 billion in export financing in 2020, supporting U.S. businesses in expanding to international markets. Additionally, consider private funding sources like venture capital or export credit agencies. According to the EXIM Bank, companies utilizing export financing grow their revenues 30% faster than those that don’t.
X. Finding and Working with Distributors
How to Find Distributors in China
To find distributors in China, start by leveraging online platforms like Alibaba and Global Sources, which list thousands of distributors and provide detailed profiles. According to Statista, Alibaba had 960 million active users in 2020, making it a key platform for finding business partners. Additionally, attend trade shows such as the Canton Fair, which attracts over 25,000 exhibitors and 200,000 buyers from around the world. The U.S. Commercial Service offers matchmaking services to connect you with potential distributors in China. Using these resources can significantly enhance your chances of finding reliable partners.
Evaluating and Selecting the Right Partners
Evaluating and selecting the right partners is crucial for successful market entry. Begin by conducting due diligence to assess the distributor’s reputation and financial stability. A report by PwC found that 60% of companies faced challenges in China due to inadequate partner selection. Request references and check their track record with other foreign brands. Evaluate their distribution network and capacity to ensure they can handle your product effectively. Look for distributors with experience in your industry and familiarity with your target market. McKinsey reports that 70% of successful market entries in China were facilitated by local partners with deep market knowledge.
Building Strong Distributor Relationships
Building strong relationships with your distributors is key to long-term success. Establish clear and transparent communication channels from the start. Regularly visit your distributors and engage in face-to-face meetings to build trust and understand their challenges. Provide comprehensive training and support to ensure they are well-equipped to promote and sell your products. Incentivize your distributors with performance-based rewards to motivate them to achieve sales targets. According to Harvard Business Review, companies that invest in strong distributor relationships see a 25% increase in market performance compared to those that don’t.
XI. Navigating China Import Regulations
Detailed Guide to China’s Import Regulations for Exporters
Navigating China’s import regulations is crucial for exporters. First, familiarize yourself with the Customs Law of the People’s Republic of China, which outlines the procedures for importing goods, including documentation requirements. Exporters must submit a Bill of Lading, Commercial Invoice, and a Packing List. Certain products require specific certifications; for instance, electronics need the China Compulsory Certification (CCC) mark. In 2020, China imported goods worth $2.4 trillion, illustrating the complexity and volume of trade regulations exporters must navigate.
Ensuring Compliance with Import Rules
Ensuring compliance with import rules is essential to avoid delays and penalties. Start by verifying that your product meets the Chinese National Standards (GB standards). These standards cover everything from product safety to labeling requirements. According to the General Administration of Customs China (GACC), non-compliance can result in fines or shipment rejections. Utilize China Inspection and Quarantine (CIQ) services to pre-inspect your goods before shipment. Maintaining compliance helps streamline customs clearance and prevents potential legal issues. In 2020, the GACC reported that 5% of imported goods were rejected due to non-compliance.
Handling Regulatory Changes
Handling regulatory changes is a constant challenge for exporters. China frequently updates its import regulations, affecting various industries. For instance, in 2018, China revised its e-commerce law, significantly impacting cross-border e-commerce operations. To stay updated, subscribe to industry newsletters and join trade associations like the China-Britain Business Council (CBBC). Implement a regulatory monitoring system to track changes and adjust your operations accordingly. According to the World Bank, staying informed and adaptable can reduce regulatory compliance costs by up to 30%. By staying informed and adaptable, you can effectively manage regulatory changes and maintain smooth business operations.
Leveraging Qianhai and MCC Qianhai for Efficient Exporting
Introduction to Qianhai Free Trade Zone
The Qianhai Free Trade Zone is a key area for international business and trade in China. Located in Shenzhen, it is strategically positioned within the Greater Bay Area, offering unique advantages for businesses looking to enter the Chinese market. The zone is designed to facilitate trade, investment, and innovation with preferential policies and world-class infrastructure.

Key Benefits of the Qianhai Free Trade Zone
- Strategic Location:
- Situated in Shenzhen, Qianhai is part of the Greater Bay Area, which includes major economic hubs like Hong Kong and Guangzhou. This location provides excellent connectivity to both domestic and international markets.
- Preferential Policies:
- Qianhai offers numerous incentives, including tax reductions, simplified customs procedures, and support for cross-border e-commerce. These policies are designed to attract foreign investment and streamline business operations.
- Advanced Infrastructure:
- The zone is equipped with state-of-the-art infrastructure, including ports, logistics centers, and business facilities. This ensures efficient handling of goods and services, reducing operational costs and transit times.
- Financial Services:
- Qianhai is a hub for financial innovation, offering various financial services and products. Businesses can access favorable financial policies, including easier cross-border capital flow and financing options.
- Innovation and Development:
- The zone encourages innovation with support for technology and research-based companies. It hosts numerous research institutions and provides resources for startups and established tech companies.
Introduction to MCC Qianhai
 MCC Qianhai is a pivotal platform within the Qianhai Free Trade Zone, operated by FS International Limited in collaboration with China Merchants Bonded Logistics. MCC Qianhai serves as a Multi-Country Consolidation (MCC) center, facilitating flexible and efficient operations for international LCL (Less-than-Container Load) transshipments.
MCC Qianhai is a pivotal platform within the Qianhai Free Trade Zone, operated by FS International Limited in collaboration with China Merchants Bonded Logistics. MCC Qianhai serves as a Multi-Country Consolidation (MCC) center, facilitating flexible and efficient operations for international LCL (Less-than-Container Load) transshipments.
Key Benefits of Using MCC Qianhai
- Integrated Logistics Network:
- MCC Qianhai benefits from Qianhai’s robust logistics network, providing seamless connections between Hong Kong, the Pearl River Delta, and other major regions. This supports both inbound and outbound LCL cargo efficiently.
- Advanced Facilities:
- With state-of-the-art warehousing and consolidation facilities, MCC Qianhai ensures high efficiency in cargo handling and storage. The platform supports various value-added services such as labeling, pick-pack, and kitting.
- Customs Supervision and Support:
- MCC Qianhai works closely with Shekou Customs to streamline customs procedures, providing a supervised environment that facilitates quicker customs clearance and reduces the risk of delays.
- Preferential Policies:
- Operating within the Qianhai Free Trade Zone, MCC Qianhai benefits from the zone’s preferential policies, including tax exemptions under RCEP and ASEAN agreements, making it an attractive option for cost optimization.
Services Offered by MCC Qianhai
- International Consolidation and Transshipment:
- MCC Qianhai excels in consolidating cargo from multiple countries, offering a reliable transshipment hub that enhances the efficiency of global logistics operations.
- Direct Import and Export Services:
- The platform supports direct LCL shipments from various international origins to China, ensuring timely and cost-effective delivery to the final destination.
- Door-to-Door Delivery:
- Comprehensive door delivery services are available, covering Guangdong Province and extending to other regions, ensuring a smooth end-to-end supply chain.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Example 1: Electronics Exporter: An electronics company used MCC Qianhai to consolidate shipments from various suppliers in Southeast Asia. By leveraging MCC Qianhai’s facilities and services, the company reduced transit times by 20% and saved on customs clearance costs, resulting in a more efficient supply chain and improved market competitiveness in China.
Example 2: Agricultural Products: A U.S. exporter of organic food products utilized MCC Qianhai for its inbound logistics to China. The strategic location and efficient customs processes at Qianhai enabled the company to maintain product freshness and meet stringent Chinese import standards, facilitating successful market entry.
Incorporating Qianhai and MCC Qianhai into your export strategy can significantly enhance your logistics efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure smoother market entry into China. By leveraging the strategic location, advanced infrastructure, and comprehensive service offerings of Qianhai and MCC Qianhai, exporters can gain a competitive edge in the dynamic Chinese market.
Special Note
It is important to note that MCC Qianhai is part of the same group as HAI International Holding, the site where this guide is published. This relationship ensures optimal synergy between transportation and logistics services, providing exporters with an integrated and seamless solution for their export needs.
XII. Export Strategies and Market Expansion
Developing Long-Term Export Strategies
To ensure sustained success in the Chinese market, developing long-term export strategies is crucial. Start by setting clear objectives aligned with your business goals. Conduct comprehensive market research to understand consumer trends and identify growth opportunities. According to a McKinsey report, companies with a well-defined export strategy see a 30% increase in market share compared to those without one. Additionally, establish a robust supply chain to handle increased demand and ensure consistent product quality. Invest in brand building to establish a strong presence and foster customer loyalty in China.
Scaling Your Business in the Chinese Market
Scaling your business in China requires a strategic approach. Begin by expanding your distribution network to cover more regions. Partner with local distributors who have a deep understanding of the market dynamics. According to the International Trade Administration, companies that partner with local firms experience a 50% faster market penetration. Focus on product localization to meet local preferences and regulatory standards. This might involve modifying product features, packaging, or even pricing strategies. Lastly, invest in customer service to build trust and satisfaction among Chinese consumers.
Leveraging Digital Platforms for Market Expansion
Leveraging digital platforms is essential for market expansion in China. E-commerce platforms like Alibaba, JD.com, and Pinduoduo dominate the market, with Alibaba alone accounting for over 50% of China’s e-commerce sales in 2020. Utilize these platforms to reach a broader audience and streamline the sales process. Implement digital marketing strategies on popular social media platforms like WeChat and Weibo. These platforms allow for targeted advertising and direct engagement with consumers. According to a study by Bain & Company, brands that actively engage on social media see a 20% increase in customer engagement. Embrace data analytics to monitor performance and optimize your strategies continuously. By effectively using digital platforms, you can significantly enhance your market presence and drive growth.
XIII. Risks and Solutions
Identifying the Risks
When exporting to China, it’s crucial to identify potential risks that could impact your business. One significant risk is regulatory changes. China frequently updates its trade and import regulations, which can affect compliance and market access. According to a report by PwC, 60% of companies face challenges due to unexpected regulatory changes. Another risk is intellectual property (IP) theft. Despite improvements in IP laws, counterfeiting remains a concern. The U.S. Chamber of Commerce reports that China accounted for 63% of global counterfeit goods in 2020. Additionally, cultural misunderstandings can pose risks, leading to miscommunications and damaged relationships. The Economist Intelligence Unit found that 45% of foreign businesses in China encounter difficulties due to cultural differences.
Mitigation Solutions
To mitigate these risks, several strategies can be employed. For regulatory changes, staying informed and proactive is key. Subscribe to industry newsletters and engage with trade associations like the China-Britain Business Council (CBBC) to stay updated on regulatory changes. According to the World Bank, companies that stay informed on regulatory changes can reduce compliance costs by up to 30%. For IP protection, register your trademarks and patents in China and use local legal resources to enforce your rights. According to the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), firms that register their IP in China see a 30% reduction in infringement cases. To address cultural misunderstandings, invest in cultural training for your team. Understanding Chinese business etiquette and communication styles can significantly improve your interactions and relationships. By implementing these mitigation solutions, you can navigate the risks of exporting to China more effectively.
Conclusion
Recap of Key Points
Exporting to China offers immense opportunities but requires careful planning and understanding of the market. We discussed the importance of assessing your business readiness, developing a robust export strategy, and navigating China’s complex import regulations. Building strong relationships with local distributors and understanding cultural nuances can significantly enhance your success. Additionally, we covered best practices for trade compliance, leveraging digital platforms, and identifying and mitigating risks.
Final Tips
As you venture into the Chinese market, remember to stay informed about regulatory changes and market trends. According to the World Bank, staying updated on regulations can reduce compliance costs by up to 30%. Invest in cultural training for your team to avoid misunderstandings and build stronger business relationships. A study by the Economist Intelligence Unit found that 45% of foreign businesses in China encounter difficulties due to cultural differences. Protect your intellectual property by registering trademarks and patents in China. According to WIPO, firms that register their IP see a 30% reduction in infringement cases. Utilize local resources and engage with trade associations to stay ahead of potential challenges. Maintaining flexibility and adaptability in your strategy will help you navigate the dynamic Chinese market more effectively.
Additional Resources
To further assist you in your export journey, consider the following resources:
China-Britain Business Council (CBBC)
The China-Britain Business Council (CBBC) provides extensive insights and support for businesses looking to enter the Chinese market. They offer a range of services including market research, strategy development, and networking opportunities. CBBC’s reports and briefings are invaluable for understanding the latest market trends and regulatory updates. Their advisory services help businesses navigate the complexities of the Chinese market, ensuring compliance and strategic alignment.
U.S. Commercial Service
The U.S. Commercial Service is a government agency that helps U.S. businesses export their goods and services globally. They offer matchmaking services to connect U.S. exporters with potential Chinese partners and distributors. Their market research reports provide detailed information on Chinese industries and consumer behavior. Additionally, the U.S. Commercial Service conducts trade missions and events that facilitate direct engagement with key stakeholders in China, offering a practical route to establishing business relationships.
World Bank
The World Bank is an excellent resource for data and reports on global trade regulations and market conditions. Their publications cover a wide range of topics, from economic forecasts to regulatory environments. The World Bank’s Ease of Doing Business index and related reports provide insights into China’s business climate, helping exporters understand the regulatory landscape and operational challenges. Utilizing these resources can help businesses make informed decisions and mitigate risks.
Alibaba and Global Sources
Alibaba and Global Sources are leading online platforms for finding reliable distributors and partners in China. Alibaba is the world’s largest e-commerce marketplace, offering access to millions of products and suppliers. It provides tools for vetting suppliers, managing logistics, and ensuring secure transactions. Global Sources specializes in B2B trade and offers a comprehensive database of verified suppliers. Both platforms feature extensive reviews, ratings, and transaction histories, which are crucial for due diligence.
McKinsey & Company Reports
McKinsey & Company publishes in-depth analysis and insights on the Chinese market and consumer behavior. Their reports cover a broad spectrum of industries, providing data-driven insights into market dynamics, consumer trends, and competitive landscapes. McKinsey’s expertise in strategic consulting is reflected in their detailed case studies and practical recommendations, making their reports a valuable tool for exporters looking to develop and refine their market strategies.
Trade Associations and Chambers of Commerce
Trade associations and chambers of commerce such as the American Chamber of Commerce in China (AmCham China) and the European Union Chamber of Commerce in China offer extensive resources and support for exporters. They provide networking opportunities, advocacy, and up-to-date information on regulatory changes and market conditions. Membership in these organizations can offer valuable connections and insights.
Export-Import Bank of the United States (EXIM)
The Export-Import Bank of the United States (EXIM) provides financial assistance to U.S. exporters through loan guarantees, direct loans, and export credit insurance. These financial products can help mitigate the risks associated with international trade and provide working capital for exporters. EXIM’s services are particularly useful for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) looking to expand into the Chinese market.
Local Government Resources
Local government resources such as the China Council for the Promotion of International Trade (CCPIT) offer support for foreign businesses entering the Chinese market. CCPIT provides information on trade policies, market conditions, and legal requirements. They also organize trade fairs and business missions to facilitate connections between foreign and Chinese companies.
Legal and Consulting Firms
Engaging with legal and consulting firms that specialize in Chinese market entry can provide tailored advice and support. Firms such as Baker McKenzie and Dezan Shira & Associates offer services ranging from regulatory compliance and intellectual property protection to market entry strategy and business setup.
By leveraging these resources and following the guidelines outlined in this guide, you can position your business for success in China’s lucrative market. These resources provide critical information, strategic insights, and practical tools that can help you navigate the complexities of exporting to China, ensuring a well-informed and strategic approach to market entry.
Annexes
Glossary of Key Terms
Understanding key terms is crucial for navigating the complexities of exporting to China. Here are some essential terms:
- Guanxi: The concept of building networks and relationships, which is vital in Chinese business culture.
- CIQ (China Inspection and Quarantine): The authority responsible for inspecting and quarantining imported goods.
- CCC (China Compulsory Certification): A mandatory safety certification for products sold in China.
- Bill of Lading: A legal document between the shipper and carrier detailing the type, quantity, and destination of goods being shipped.
- Incoterms: International commercial terms defining responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
- Harmonized System (HS) Code: A standardized numerical method of classifying traded products, crucial for customs and tariff purposes.
- Tariff Rate Quota (TRQ): A system that allows a set amount of goods to be imported at a lower tariff rate, with higher tariffs applied to amounts exceeding the quota.
- Export License: An official document granting permission to export specific goods to certain destinations.
- Certificate of Origin: A document certifying the country in which the goods were manufactured, often required for customs clearance.
- Letter of Credit (LC): A guarantee from a bank ensuring the seller will receive payment under specific conditions.
- Customs Declaration Form: A document that provides details about goods being imported or exported, required by customs authorities.
- Free Trade Agreement (FTA): A pact between two or more countries to reduce trade barriers and increase trade of goods and services.
- Value-Added Tax (VAT): A tax on the added value of goods and services, which exporters must understand to ensure proper pricing and compliance.
- Non-Tariff Barriers (NTBs): Restrictions that countries use to control the amount of trade across their borders, including quotas, embargoes, sanctions, and levies.
- Trade Barriers: Measures such as tariffs, duties, and quotas that governments impose to protect domestic industries from foreign competition.
By familiarizing yourself with these key terms, you can better navigate the regulatory and logistical challenges of exporting to China.
Contacts and Useful Resources
Having the right contacts and resources can significantly ease the export process:
- China-Britain Business Council (CBBC): Offers market research and networking opportunities. Website
- U.S. Commercial Service: Provides matchmaking services and market insights.
- World Bank: Source for data on global trade regulations. Website
- Alibaba and Global Sources: Platforms for finding distributors and partners. Alibaba | Global Sources
- McKinsey & Company: Publishes detailed market analysis reports. Website
Sample Export Documents
Understanding the purpose and details of essential export documents is crucial for smooth international trade. Here are some key documents you will need:
Commercial Invoice
A Commercial Invoice is a critical document in international trade, as it includes all pertinent details of the sale transaction. This document serves as a record of the sale between the exporter and the importer. Key elements include:
- Buyer and Seller Information: Names, addresses, and contact details.
- Item Description: Detailed description of the goods, including quantity, unit price, and total price.
- Terms of Sale: Payment terms, delivery terms, and Incoterms.
- Date of Invoice: When the invoice was issued.
- Shipping Details: Mode of transport, shipping date, and delivery date. This document is used by customs authorities to determine the correct duties and taxes.
Bill of Lading
A Bill of Lading is both a receipt and a contract. It outlines the terms under which the goods are being transported and serves as proof that the carrier has received the goods. Important components include:
- Shipper and Carrier Information: Names and contact details.
- Consignee Information: The party to whom the goods are being delivered.
- Description of Goods: Details about the nature, quantity, and condition of the goods.
- Shipping Instructions: Terms of delivery and any special handling instructions.
- Signature: The carrier’s signature, acknowledging receipt of the goods. This document is essential for the legal transfer of goods from the exporter to the importer.
Packing List
A Packing List provides detailed information about the contents of each package in the shipment. It helps in verifying the contents during transportation and at customs. Key details include:
- Packaging Types: Description of each package type (e.g., boxes, pallets).
- Weights and Dimensions: Gross and net weight, along with dimensions of each package.
- Contents of Each Package: Specific items contained in each package.
- Shipping Marks and Numbers: Identification marks and numbers on the packages. Customs authorities use this document to inspect the shipment and ensure it matches the commercial invoice.
Certificate of Origin
A Certificate of Origin certifies the country where the goods were manufactured. This document is often required to determine the applicable tariffs and to comply with trade agreements. It includes:
- Exporter and Importer Information: Names and addresses.
- Product Details: Description of goods, including HS codes.
- Country of Origin: Declaration of the manufacturing country.
- Certification by an Authorized Body: Typically certified by a chamber of commerce or trade association. This document is crucial for benefiting from preferential tariff rates under Free Trade Agreements (FTAs).
Export License
An Export License is a government-issued document that grants permission to export specific goods to certain destinations. Some products, especially those considered strategically sensitive or dual-use (civilian and military), require this license. Key points include:
- Exporter Information: Name, address, and registration details.
- Goods Description: Detailed description of the goods, including specifications and end-use.
- Destination: Countries to which the goods are being exported.
- Validity Period: The time frame within which the export can occur. Obtaining this license ensures that the export complies with national and international regulations, and prevents illegal trade.
By understanding and correctly preparing these documents, exporters can ensure compliance with international trade regulations, smooth customs clearance, and successful delivery of goods to their destinations.
FAQ: The Ultimate Guide to Exporting to China
What are the key benefits of exporting to China?
Exporting to China offers numerous benefits, including access to a large and growing market with over 1.4 billion consumers, increasing demand for high-quality imported goods, and opportunities to diversify revenue streams. Additionally, the Chinese government's Belt and Road Initiative aims to enhance trade relations, creating favorable conditions for international businesses.
How can I find reliable distributors in China?
To find reliable distributors in China, leverage online platforms like Alibaba and Global Sources, attend trade shows such as the Canton Fair, and utilize services from the U.S. Commercial Service. Conduct thorough due diligence, including checking references and evaluating their distribution network.
What are the common challenges of exporting to China?
Common challenges include navigating regulatory compliance, protecting intellectual property, understanding and adapting to local competition, and managing logistics and supply chains. Staying informed about regulatory changes and investing in IP protection are crucial.
How can I ensure compliance with Chinese import regulations?
Ensure compliance by verifying product standards with Chinese National Standards (GB standards), using China Inspection and Quarantine (CIQ) services for pre-inspection, and staying updated on regulatory changes through industry newsletters and trade associations.
What strategies can help in successfully entering the Chinese market?
Successful market entry strategies include conducting thorough market research, developing a tailored export strategy, building strong relationships with local partners and distributors, and leveraging digital platforms like WeChat and Tmall for marketing and sales.
What financial considerations should I keep in mind when exporting to China?
Financial considerations include calculating costs for production, shipping, tariffs, and marketing expenses. Understand preferred payment terms in China and explore funding options from government programs like the Export-Import Bank of the United States (EXIM) and private sources such as venture capital and export credit agencies.
How can I protect my intellectual property in China?
Protect your intellectual property by registering trademarks and patents in China and using local legal resources to enforce your rights. According to WIPO, firms that register their IP in China see a 30% reduction in infringement cases.
What cultural aspects should I consider when doing business in China?
Understanding cultural aspects such as the importance of guanxi (networking and relationships), indirect communication, and respect for hierarchy is crucial. Invest in cultural training for your team to avoid misunderstandings and build stronger business relationships.



 List of Essential Export Documents
List of Essential Export Documents Understanding China Trade Compliance Requirements
Understanding China Trade Compliance Requirements










